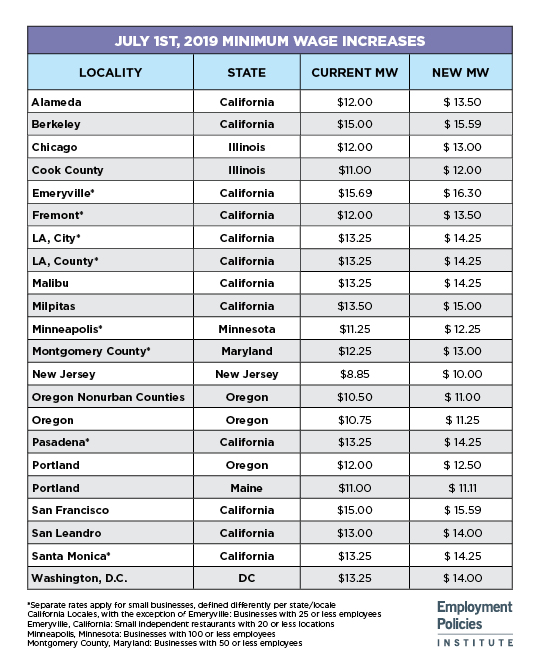
July 1st, 22 states and localities will increase their minimum wages. These increases include two states, the District of Columbia, and 19 other localities. View the full list in the chart below.
Twelve localities in California will see minimum wage increases, despite evidence that minimum wage hikes have decreased employment opportunities. A recent Employment Policies Institute study found roughly 400,000 jobs will be lost by the time California’s $15 wage mandate is fully phased in by 2022.
Evidence shows minimum wage hikes can have negative consequences, including a reduction in employee hours, lost job opportunities, or even business closures. The evidence is overwhelming and includes the following recent examples:
- After enacting a $15 minimum wage, the city of Emeryville, California announced that it would halt a wage increase planned for this summer for full-service restaurants after a city-sponsored study identified widespread job losses and business closures.
- New York City lost roughly 6,000 jobs last year as a direct result of the state and city’s rapidly rising minimum and tipped minimum wage.
- Researchers from UC Riverside found that California’s minimum wage increases have contributed to a decline in restaurant growth. For high-income regions such as Los Angeles and the Bay Area, the full-service restaurant industry will have created 30,000 fewer jobs between 2017 to 2022 as a consequence of a rapidly-rising minimum wage without a tip credit.
- According to a recent study by researchers at the University of Washington, Seattle’s $15 minimum wage has also forced many childcare centers to hike tuition costs, slash staff hours, and cut staff benefits or professional development investments.
For even more evidence, the website Facesof15.com chronicles more than 160 stories of job loss, reduced hours, and other consequences as a direct result of minimum wage increases.
Before enacting more wage hikes, policymakers should consider the negative ramifications that stem from higher wage mandates.